Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars that are used by the body for energy As carbohydrates are eaten, the digestive tract breaks them down into monosaccharide units, or glucose The glucose enters the bloodstream and travels first to the brain, which runs entirely on energy from glucoseCarbohydrates are broken down into Monosaccharaides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides These are all essential in giving the animal the appropriate amount of energy (puri, 05) The structure always follows a ratio of 121 of Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen They have a linear format In either a chain or ring formDuring digestion, carbohydrates are broken down into simple, soluble sugars that can be transported across the intestinal wall into the circulatory system to
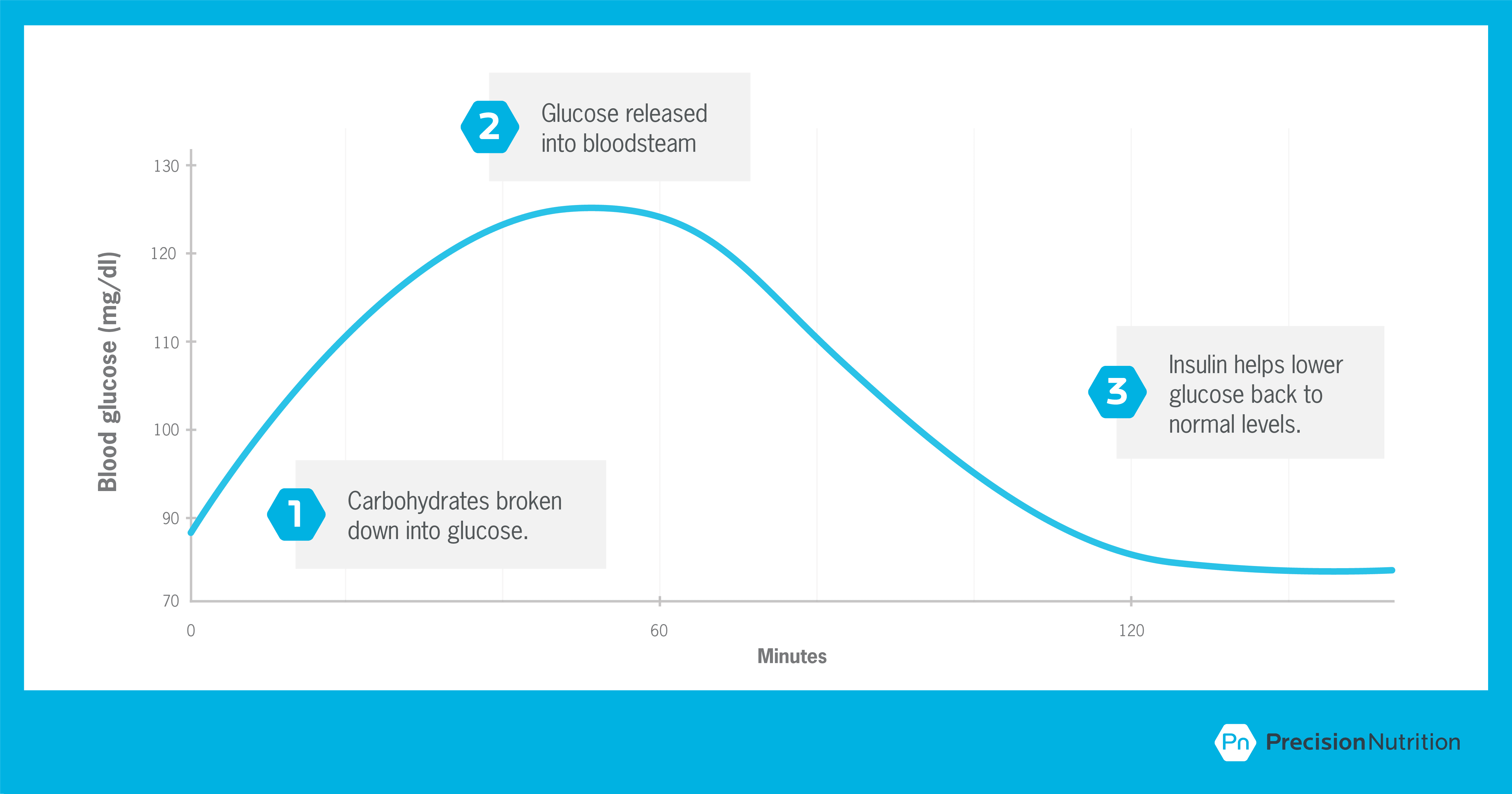
The Truth About Carbs Insulin And Weight Loss Precision Nutrition
Carbohydrates break down into what simple nutrient *
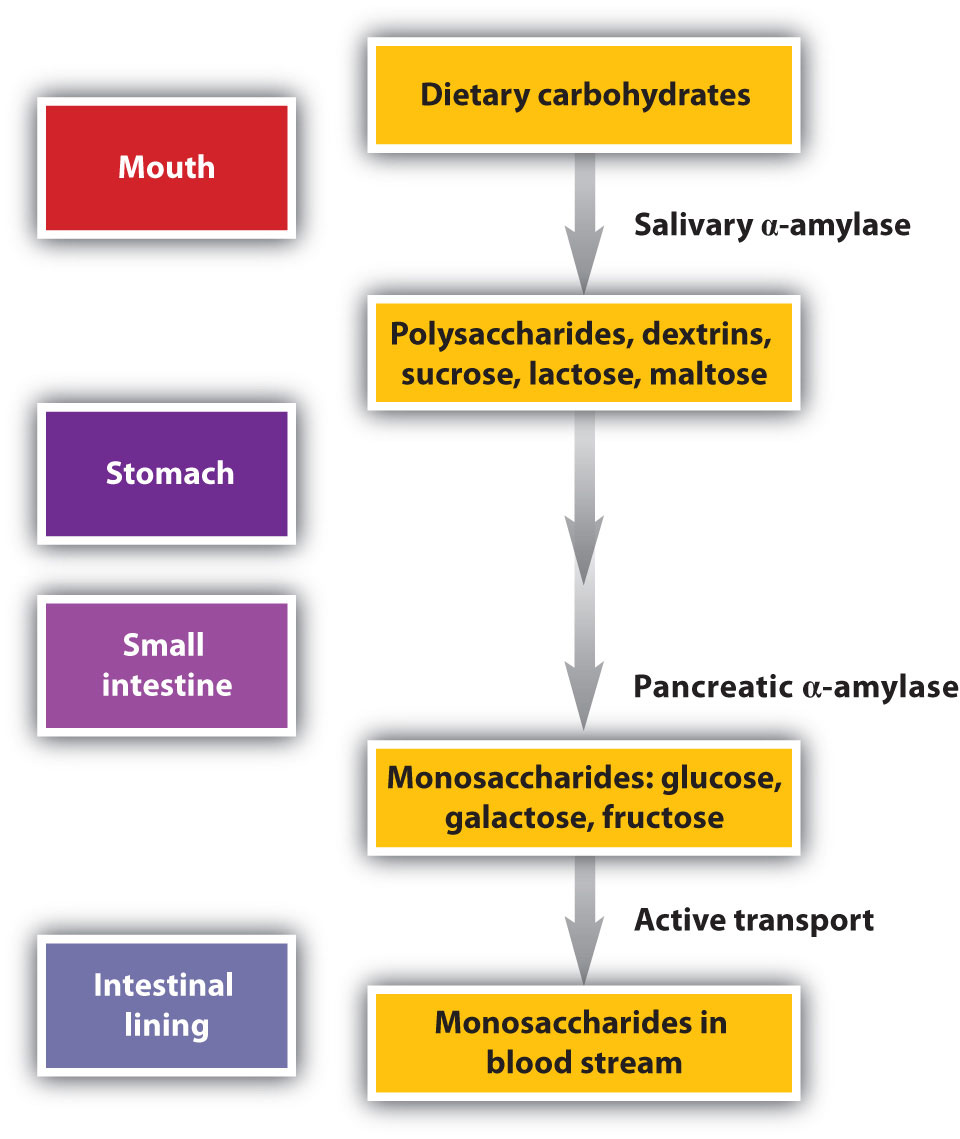
Carbohydrates break down into what simple nutrient *- Process of Carbohydrate Break down The process of carbohydrate break down starts in our mouth with an enzyme called salivary amylase It breaks the long sugars apart into smaller subunits to be absorbed, and these small, simple carbohydrates move through the cell lining of the small intestine and into the blood in capillaries that lead to the portal veinCarbohydrates (also called carbs) are a type of macronutrient found in certain foods and drinks Sugars, starches and fiber are carbohydrates Other macronutrients include fat and protein Your body needs these macronutrients to stay healthy How does the body process carbohydrates?
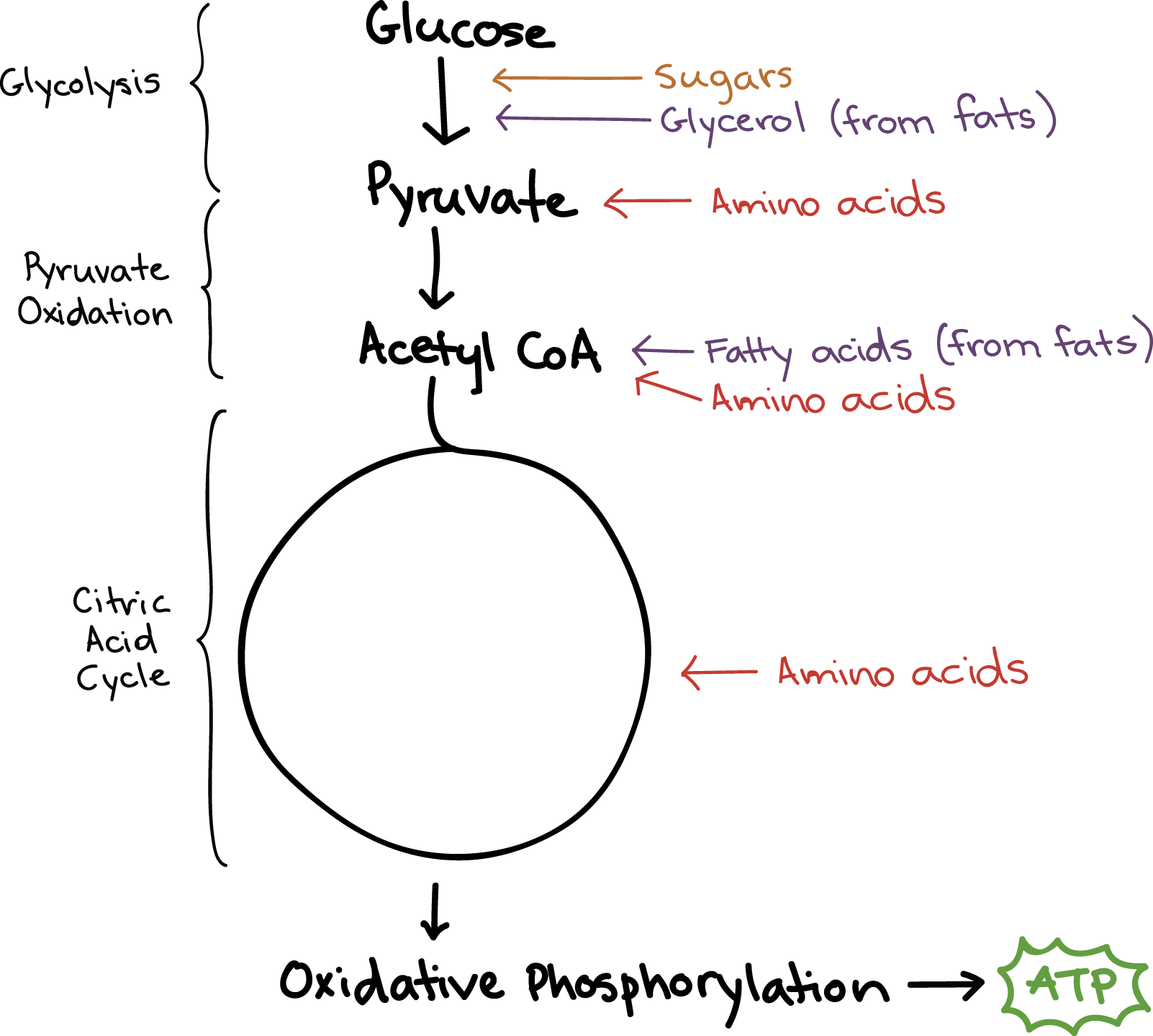



Connections Between Cellular Respiration And Other Pathways Article Khan Academy
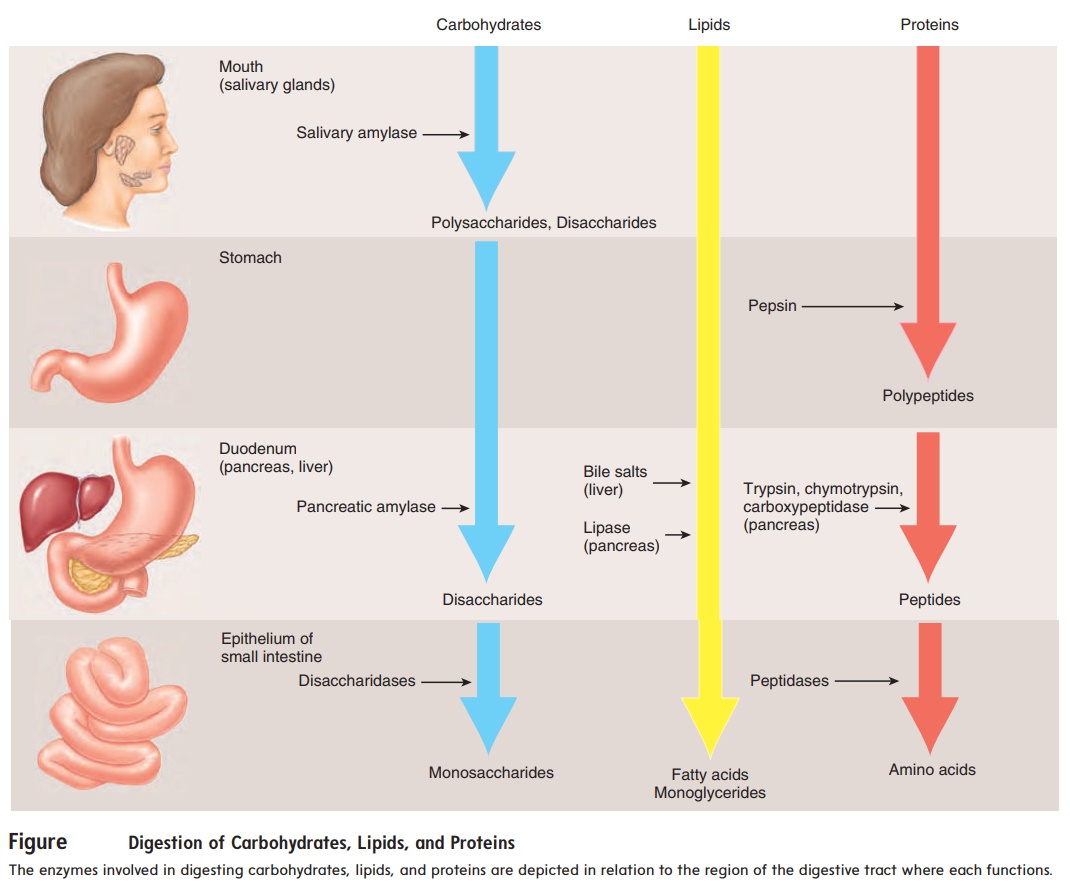
Heres the deal Both simple and complex carbohydrates break down into glucose (aka blood sugar) A simple carb is one thats comprised of one or two sugar molecules, while a complex carb contains three or more sugar molecules Fiber, on the other hand, is found in healthy carbs, but isnt digested or broken downThis enzyme starts to break the long glucose chains of starch into shorter chains, some as small as maltose (The other carbohydrates in the bread don't undergo any enzymatic digestion in the mouth) Fig 42 The enzyme salivary amylase breaks starch into smaller polysaccharides and maltose 2 Stomach Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the body can't digest Though most carbohydrates are broken down into sugar molecules, fiber cannot be broken down into sugar molecules, and instead it passes through the body undigested Fiber helps regulate the body's use of sugars, helping to keep hunger and blood sugar in check
It then converts monosaccharides mostly to glucose to provide energy for the cells' work The fibers help to regulate the passage of food through the GI system, but contribute little, if any, energy Carbs ultimately break down chemically to glucose – a simple sugar that serves as the body and brain's preferred energy source Fiber is an important component in whole food carbohydrates that slows the release of sugar into the blood, which gives you more steady energy, supports your healthy gut bacteria and immune system, and supports an What Do Complex Carbohydrates Break Down Into?
When you eat carbohydrates, your digestive system breaks down sugars and starches into glucose, which is used for energy The energy fuels physical activity and physiological functions, such as breathing and maintaining body temperature, says Oklahoma State UniversityThe body uses three main nutrients to function— carbohydrate, protein, and fat These nutrients are digested into simpler compounds Carbohydrates are used for energy (glucose) Fats are used for energy after they are broken into fatty acids Carbohydrates break down into glucose in the body Glucose moves from the bloodstream into the body's cells with the help of the hormone insulin All of the cells in a



Www Naspghan Org Files Documents Pdfs Training Curriculum Resources Physiology Series Carbohydrate Digestion Naspghan Pdf




Types Of Carbohydrates Healthy Carbs Complex Carbohydrates Are Found In Vegetables Fruits And Whole Grains Beans Legumes Sweet Potatoes And Yams Take Longer For The Body To Process Stabilize Blood Sugars Are
How the body absorbs & transports brokendown carbohydrates in the body The monosaccharide units, glucose, galactose and fructose are transported through the wall of the small intestine and then into the portal vein which then takes these elements straight to the liverAll carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, which are absorbed into the bloodstream As the sugar level rises, the pancreas releases the hormone insulin, which is needed to move sugar from the blood into the cells, where the sugar can be used as energy The carbs in some foods (mostly those that contain simple sugars and highlyHowever, it requires more process than the breakdown of simple sugar like fructose When you eat foods like toast or mashed potato, the saliva starts acting on it in the mouth The starch is broken down into maltose



Carbohydrate Digestion And Absorption The Canadian Sugar Institute



What Are Carbohydrates Quora
Humans can consume a variety of carbohydrates, digestion breaks down complex carbohydrates into a few simple monomers (monosaccharides) for metabolism glucose, fructose, mannose and galactose Glucose is distributed to cells in the tissues, where it Both simple and complex carbohydrates break down into glucose (aka blood sugar) A simple carb is one that's comprised of one or two sugar molecules, while a complex carb contains three or more When you eat carbohydrates in the form of sugar or starches, your body's goal, as noted by the Cleveland Clinic, is to break them down into the simple sugar, glucose, which it can use for energy The carbohydrates aren't really converted into glucose — they already contain the sugar in a more complex package



Stage I Of Catabolism
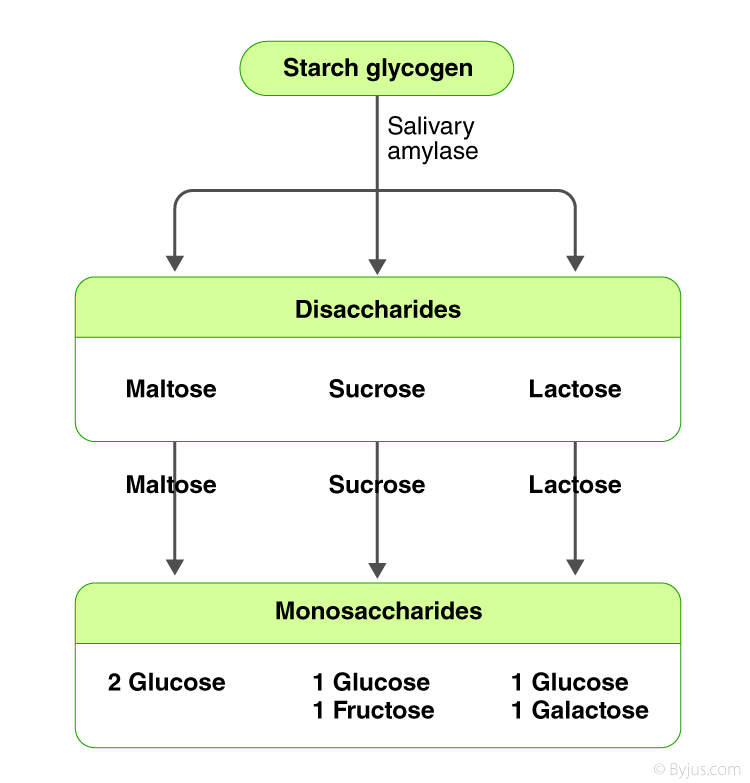



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Proteins And Lipids
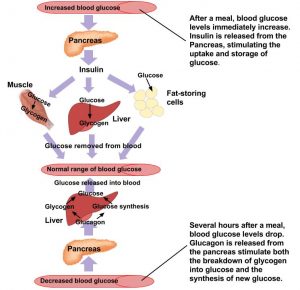
The body breaks down or converts most carbohydrates into the sugar glucose Glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream, and with the help of a hormone called insulin it travels into the cells of the body where it can be used for energy When carbohydrates are broken down into glucose within the blood, the body will Use insulin to help fuel the body's cells Use insulin to turn any remaining excess of glucose in the blood into fat for storage Carbohydrates provide energy and therefore if you have too high a level of carbohydrate in your diet this can lead to weight gain In the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, the body breaks down starches into disaccharides and disaccharides into monosaccharides;
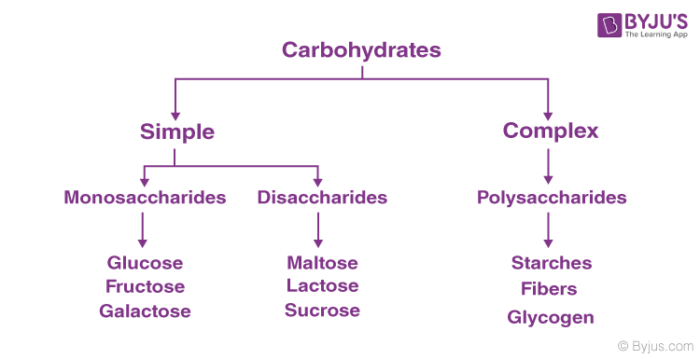



Classification Of Carbohydrates With Definition Types Structure Formula With Examples Videos




Objective Understand Carbohydrates And What Foods They Are Found In Warm Up 1 What Is Your Favorite Source Of Carbs Ppt Download
In this article we'll discuss carbohydrates break down into This is not entire article It continues KEEP READING Related Topics CARBOHYDRATES Down Into Break Related Articles Breastfeeding A Baby With Down Syndrome;Carbohydrates travel through the esophagus, stomach and enter the small intestine In the small intestine, carbohydrates get further broken down into single carbohydrate units called monosaccharide These single molecules get absorbed across the intestine wall and are sent through the blood stream In the image below, follow the numbers to see what happens to carbohydrates at each site of digestion Figure 49 The digestive system 1 – Mouth or Oral Cavity As you chew your bite of pizza, you're using mechanical digestion to begin to break it into smaller pieces and mix it with saliva, produced by several salivary glands in the oral



Where Does The Digestion Of Carbohydrates Begin What Is The Process Quora
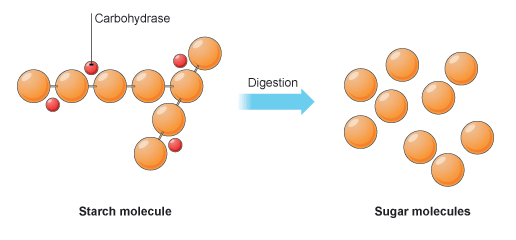



Maltase Pmg Biology
Excess carbohydrates are stored as starch in plants and as glycogen in animals, ready for metabolism if the energy demands of the organism suddenly increase When those energy demands increase, carbohydrates are broken down into constituent monosaccharides, which are then distributed to all the living cells of an organismCarbohydrates are biological molecules made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of roughly one carbon atom () to one water molecule ( ) This composition gives carbohydrates their name they are made up of carbon ( carbo ) plus water ( hydrate ) Carbohydrate chains come in different lengths, and biologically important carbohydrates Plants form starches, which are also called complex carbohydrates, by stringing together sugars When you eat starchy foods, the starches are broken down into sugars, including glucose, maltotriose



Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii
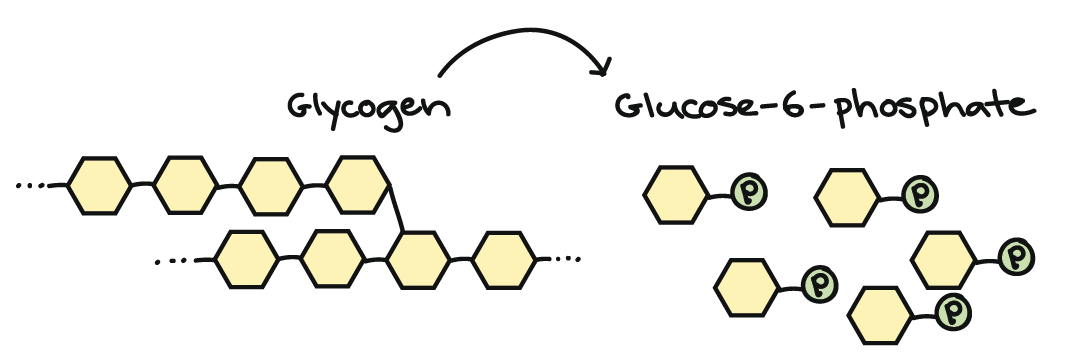



Connections Between Cellular Respiration And Other Pathways Article Khan Academy
When you eat food that contains carbohydrates, you break down the carbohydrates into a monosaccharide called _____ glucose_____ If you don't use this monosaccharide, you body can store it in the liver in the form of _____glycogen_____ 2 When your body metabolizes (breaks down) glucose, whether incompletely or completely, the first pathway Carbohydrates come from nearly all foods in your diet and eventually break down into glucose You need glucose, the simplest form of Sucrase breaks sucrose into glucose and fructose molecules Maltase breaks the bond between the two glucose units of maltose, and lactase breaks the bond between galactose and glucose Once carbohydrates are chemically broken down into single sugar units they are then transported into the inside of intestinal cells



Connections Between Cellular Respiration And Other Pathways Article Khan Academy
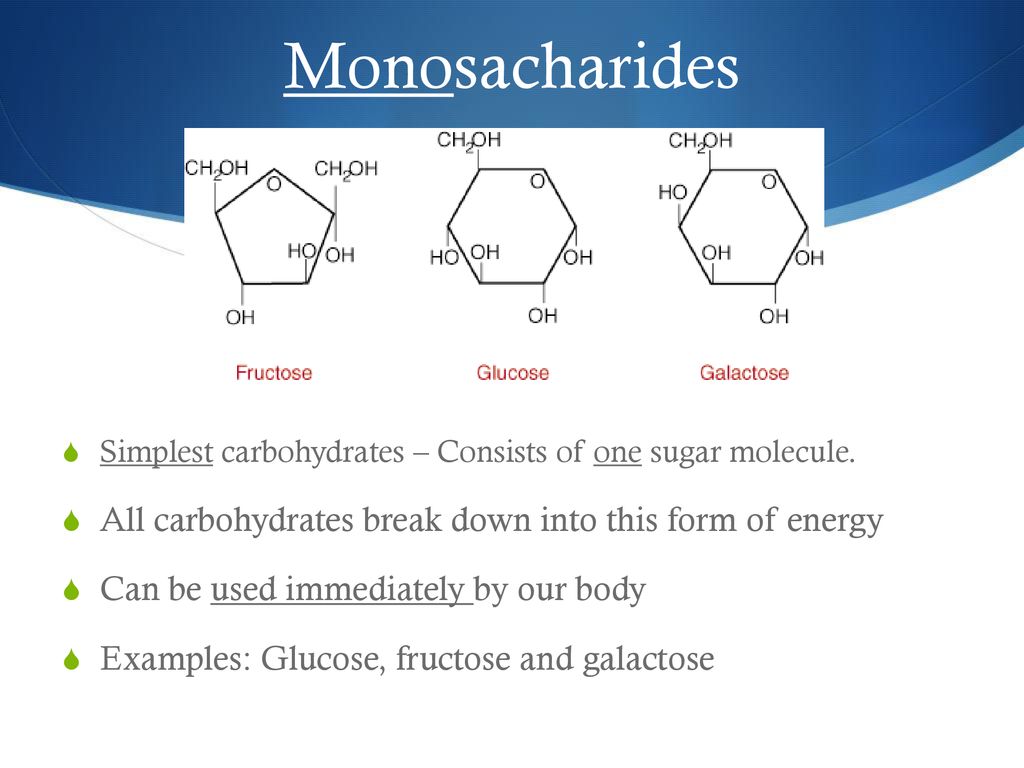



Carbohydrates Ppt Download
One of the primary functions of carbohydrates is to provide your body with energy Most of the carbohydrates in the foods you eat are digested and broken down intoHow To Lose Weight A Glass Of Milk For Breakfast Is Enough!Proteins, carbohydrates, and fats in the process of digestion, proteins are broken down into ____, while carbohydrates are broken down into ___ amino acids;




What Are Macronutrients Healthy Outcome For Teens




Carbohydrates In Pet Food Pfma
For this reason, digestive enzymes break down carbohydrates into three monosaccharides, namely glucose, galactose, and fructose Monosaccharides are transported to the liver, which turns galactose and fructose into glucose The liver then sends the produced glucose into the bloodstream, where it is transported to the cells that need energyYour digestive system breaks down carbs into glucose or blood Most grains (wheat, corn, oats, rice) and things like potatoes and plantains are high in starch Your digestive system breaks a complex carbohydrate (starch) back down into its component glucose molecules so that the glucose can enter your bloodstream It takes a lot longer to break down a starch, however




Connections Between Cellular Respiration And Other Pathways Article Khan Academy




Solved Digestion Of Carbohydrates 1 Carbohydrates Are Br Chegg Com
Sucrase breaks sucrose into glucose and fructose molecules Maltase breaks the bond between the two glucose units of maltose, and lactase breaks the bond between galactose and glucose Once carbohydrates are chemically broken down into single sugar units they are then transported into the inside of intestinal cells Simple carbs are classified as being "simple" because they EASILY break down in one simple step in your gut For example when you eat an apple, simple carbohydrate fructose molecules head directly to your small intestine From there, they quickly convert to glucose and absorb into your bloodstream through intestinal wallsCarbohydrates are broken down by the body into glucose, which can be absorbed into the bloodstream Once absorbed, glucose molecules travel in




Monosaccharides An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Who Said No Carbs Carbohydrates Bodytech By Charith Facebook
Glucose Complex carbs get broken down into glucose;Carbohydrates not used for energy or glycogen storage are converted to fat Glycaemic index The speed at which the carbohydrates in a food are digested to glucose is called the food's glycaemic index (GI) value Low GI foods are broken down slowly The glucose, or energy, from their carbohydrates is released into the blood over several hoursDuring digestion, carbohydrates are broken down into simple, soluble sugars that can be transported across the intestinal wall into the circulatory system to be transported throughout the body Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with the action of



Digestion Storyboard By Oliversmith




This Flow Chart Shows The Steps In Digestion Of Carbohydrates The Different Levels Shown Are Starch Carbohydrates Biology Biology Notes Anatomy And Physiology
4 calories in a gram of carbohydrate or protein 9 calories in a gram of fat These nutrients also differ in how quickly they supply energy Carbohydrates are the quickest, and fats are the slowest Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are digested in the intestine, where they are broken down into their basic units




Digestion Of Carbohydrates Biology For Everybody



The War On Carbohydrates Tidal Elite Performance Center
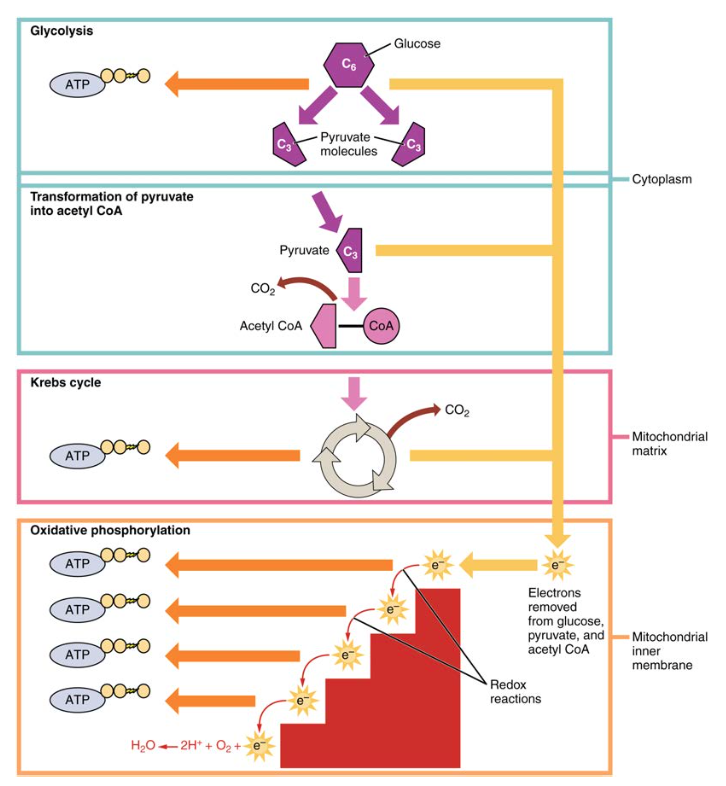



Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii




3 3 Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Medicine Libretexts




The Mysteries Of Digestion Unraveled Embracing Motherhood




Carbohydrate Their Types And Sources Carbohydrates Youtube




Carbohydrates Sugar Starch And Fiber Ppt Video Online Download



Carbohydrates How Food Works Howstuffworks




Into What Substance Do Most Carbohydrates Break Down During Digestion Study Com




Carbohydrate Chemical Reactions Britannica



Www Naspghan Org Files Documents Pdfs Training Curriculum Resources Physiology Series Carbohydrate Digestion Naspghan Pdf



Q Tbn And9gcrngedmz5p8ksahkx4mevekwbdzyga0f I1kthrenssnk8u Lpe Usqp Cau



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates



Digestion Energy And Metabolic Pathways It S A Natural Universe



1



Carbohydrates Unbelievable Facts About Carbohydrates Blog Jake
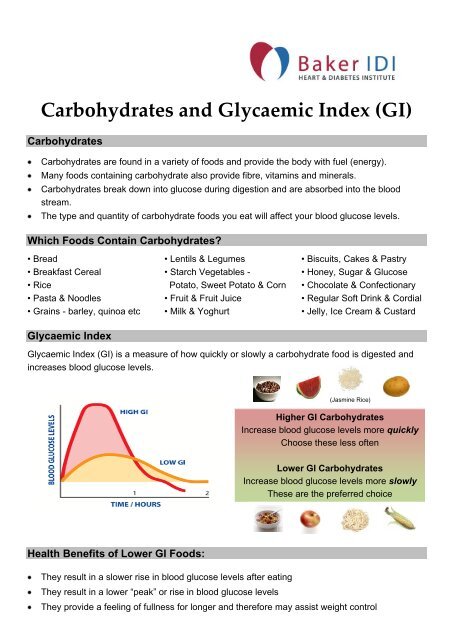



Carbohydrates And The Glycaemic Index Baker Idi




Carbohydrate Metabolism Wikipedia



Are Carbohydrates Same As Sugar Quora
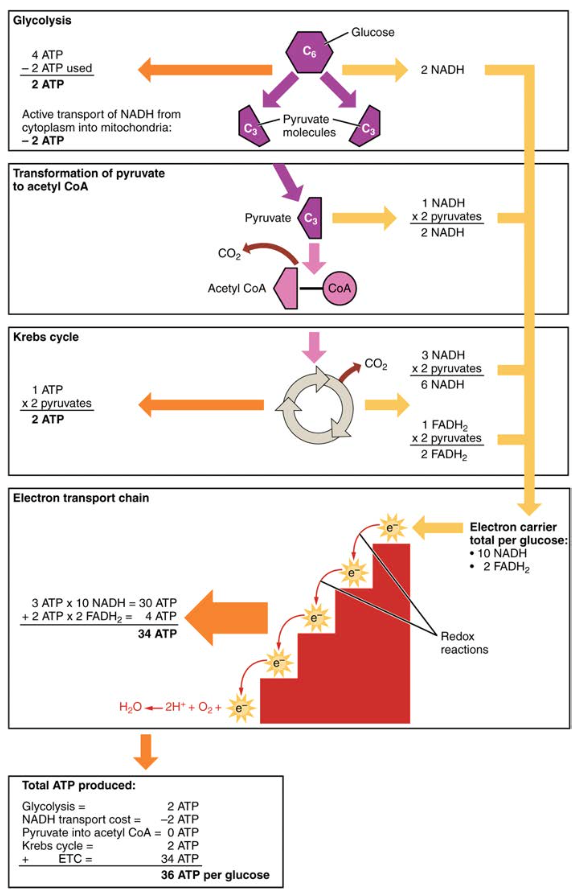



Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii
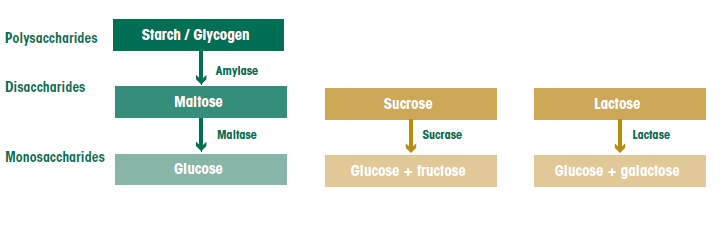



Carbohydrate Digestion And Absorption The Canadian Sugar Institute



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates




Enzymes 1 Specific 2 Carbohydrates 3 Starch 4 Protease 5 Break Down Ppt Download




Carbohydrates




The War On Carbohydrates Tidal Elite Performance Center
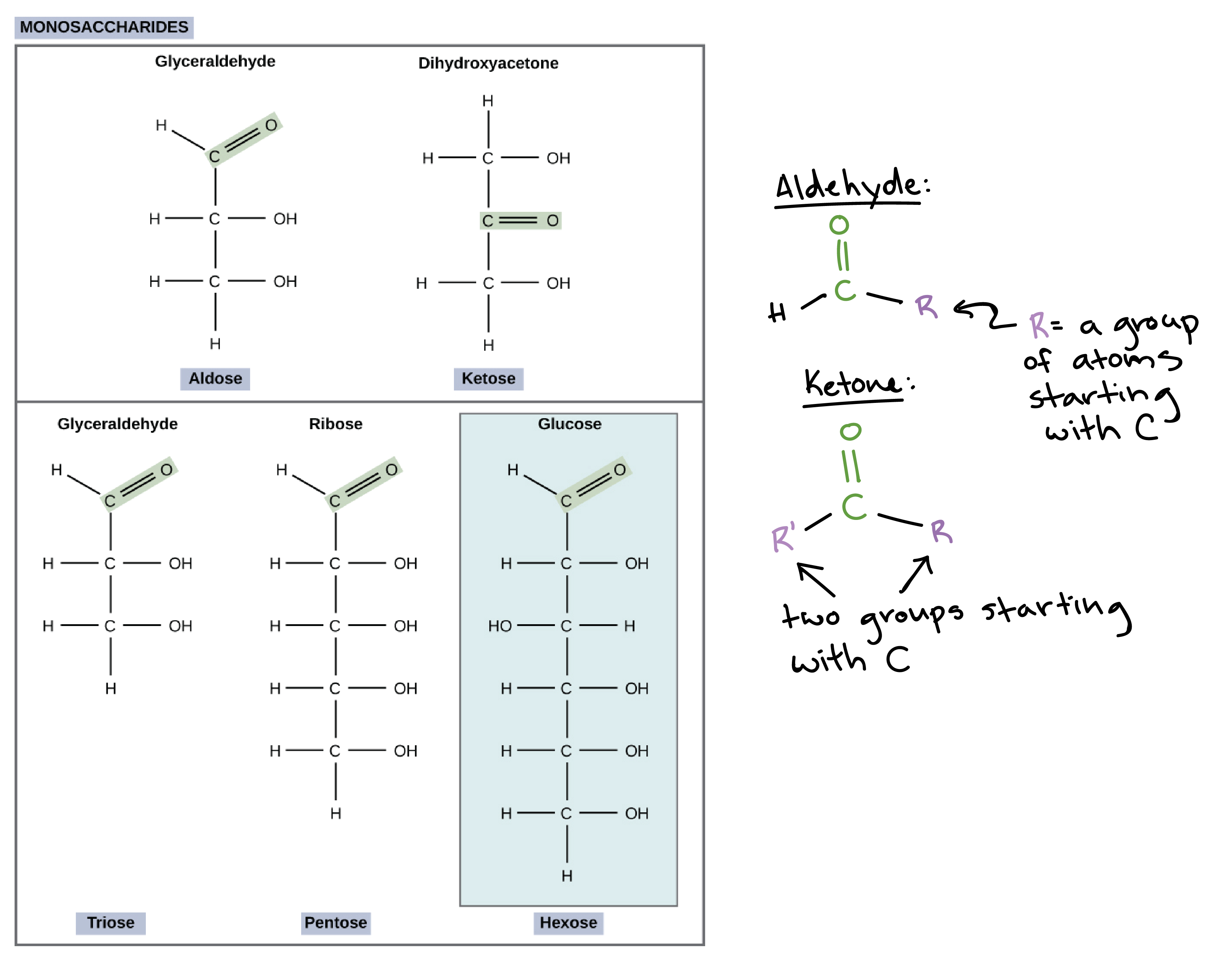



Carbohydrates Article Chemistry Of Life Khan Academy
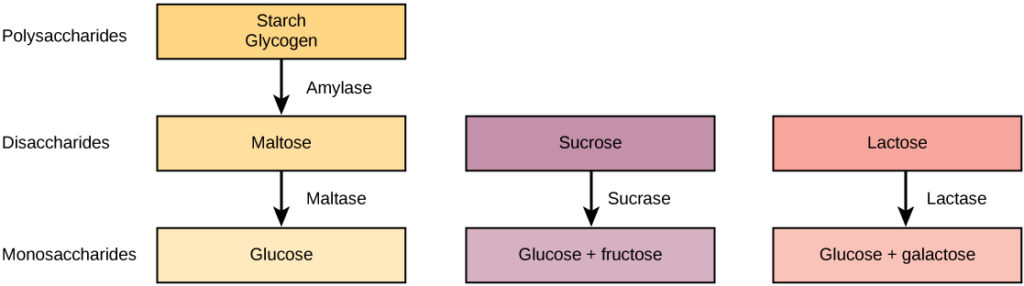



Digestive System Processes Biology For Majors Ii
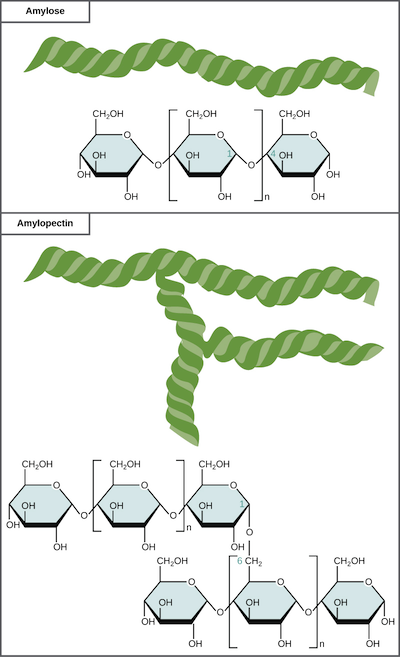



Carbohydrates Article Chemistry Of Life Khan Academy



Types Of Carbohydrates
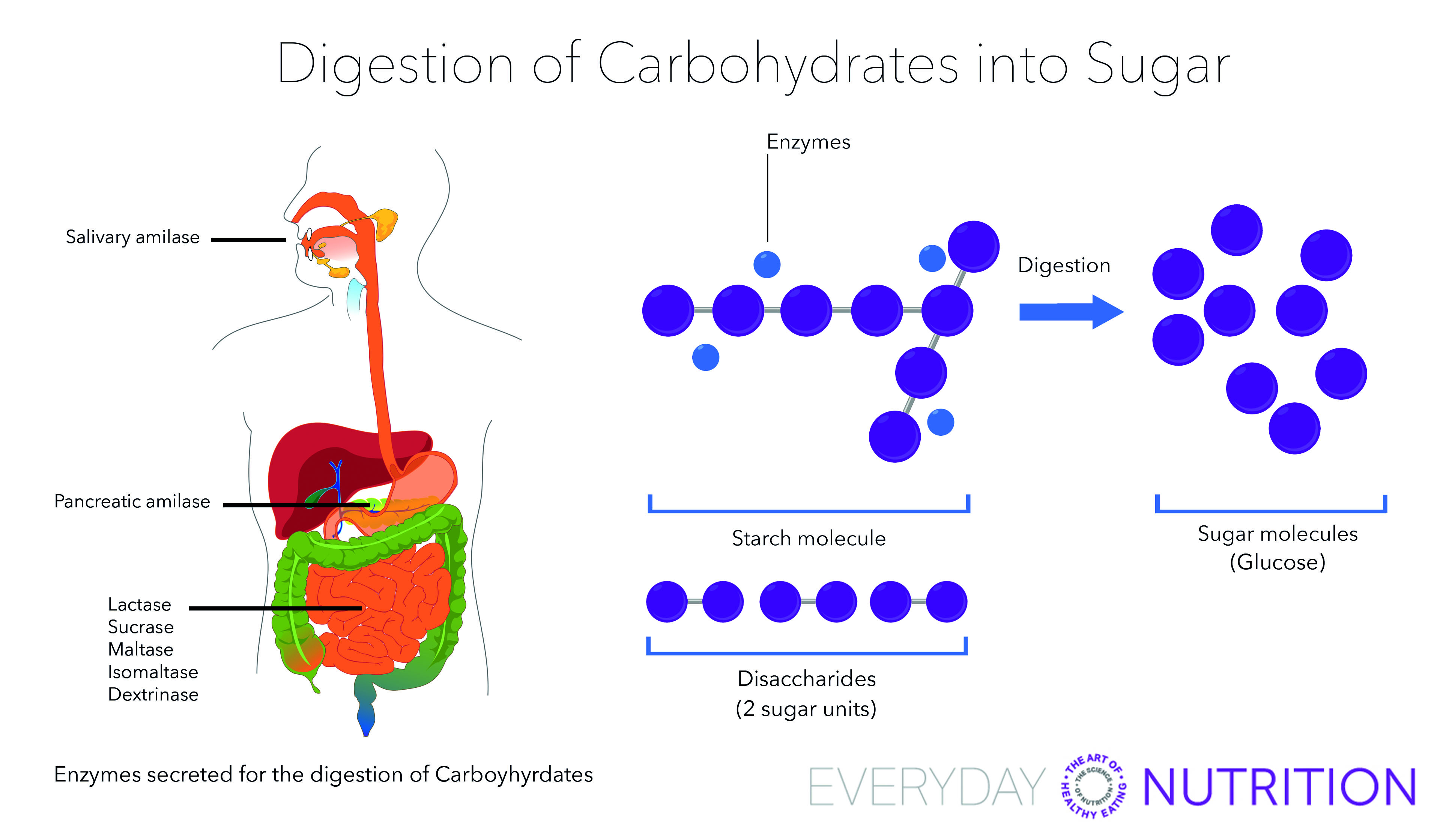



Everyday Nutrition Digestion Of Carbohydrates Into Sugar




Carbohydrates Sciencedirect




Digestion Absorption And Transport In Digestive System



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates




4 1 Introduction To Carbohydrates Medicine Libretexts
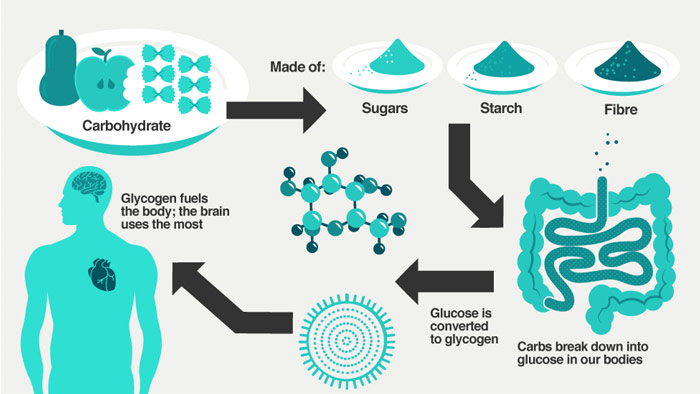



What Does Iifym Mean A Guide To Flexible Dieting For Fat Loss Heyspotmegirl Com



Types Of Carbohydrates
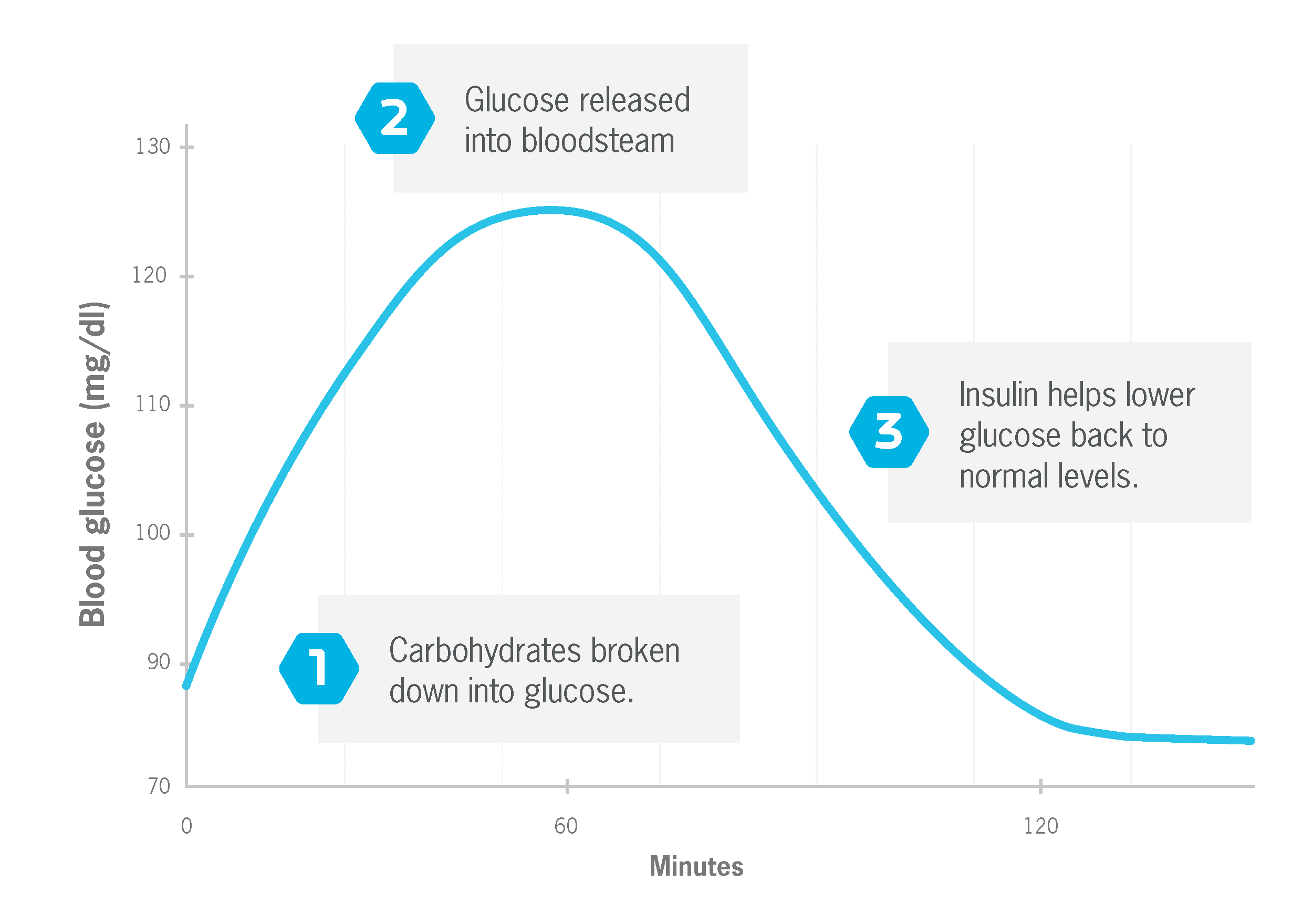



The Truth About Carbs Insulin And Weight Loss Precision Nutrition




4 2 Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Medicine Libretexts
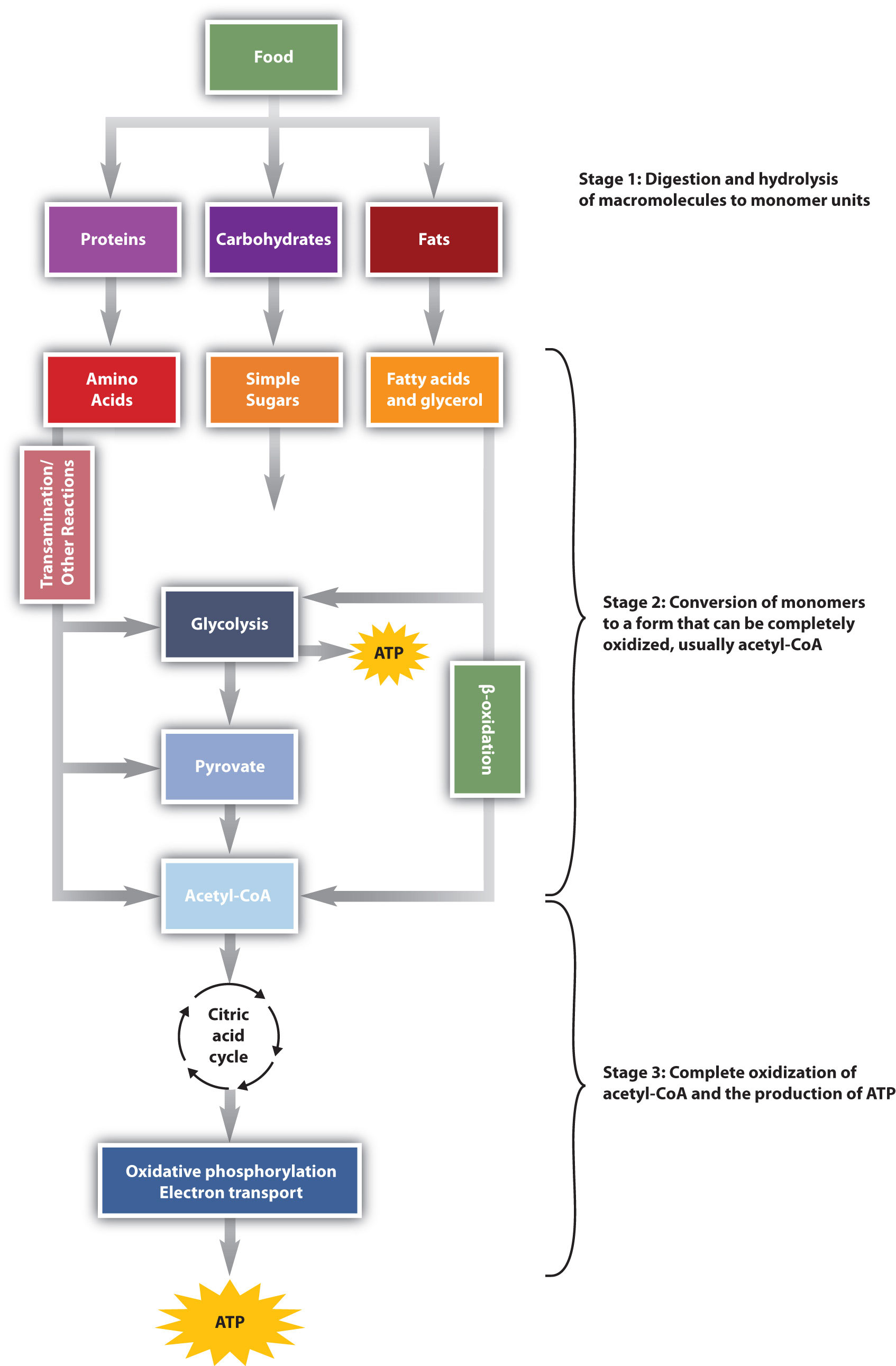



2 Stage I Of Catabolism Chemistry Libretexts
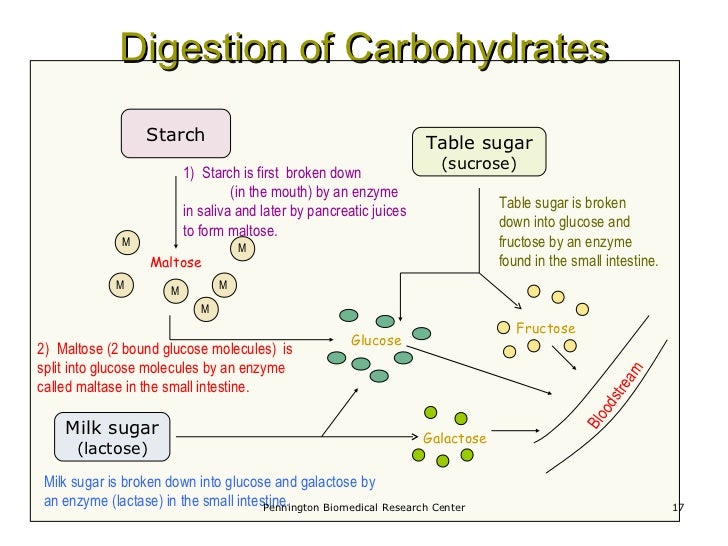



Fueling Your Body Unit 5




Digestive System Processes Biology For Majors Ii
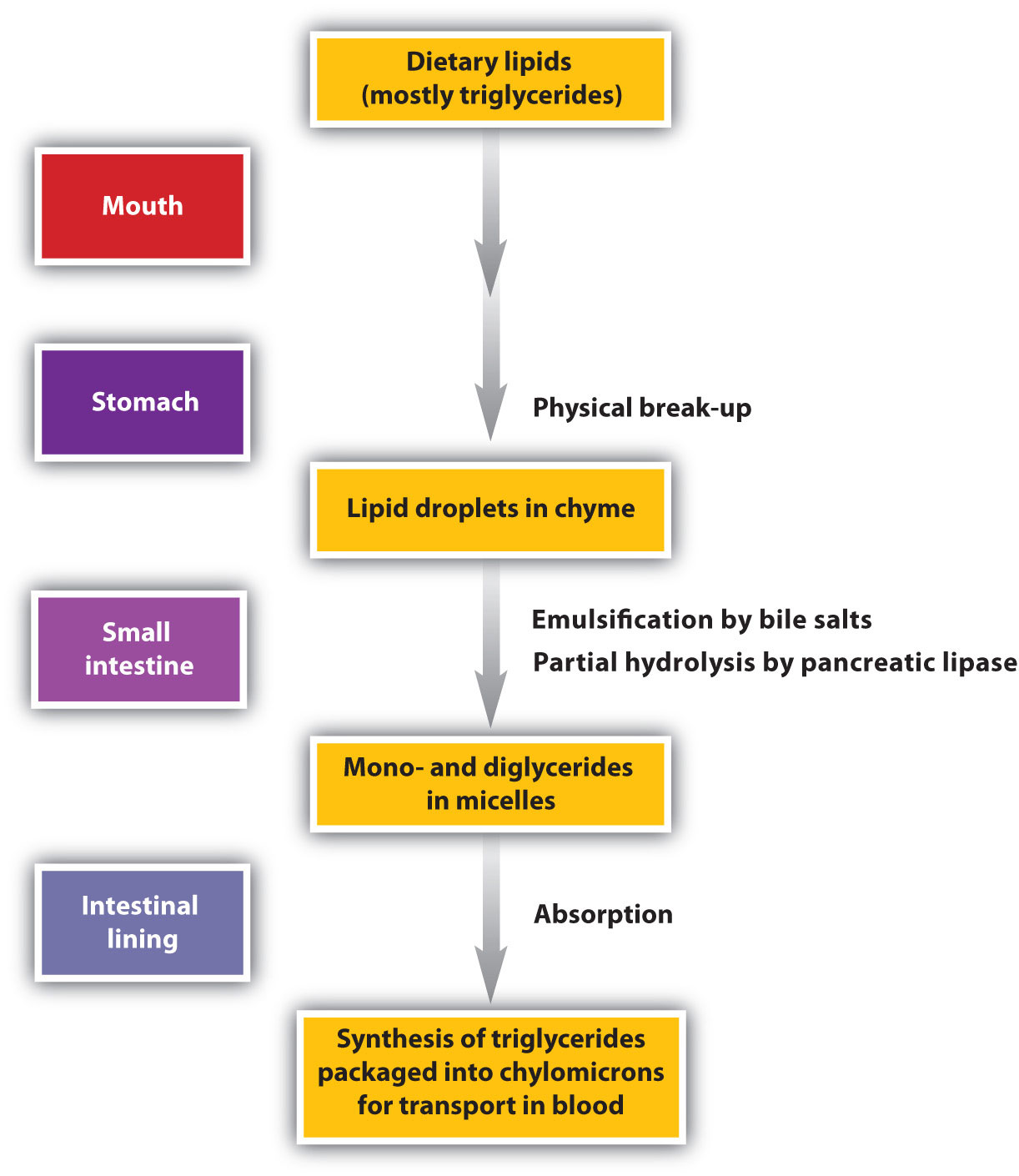



Stage I Of Catabolism
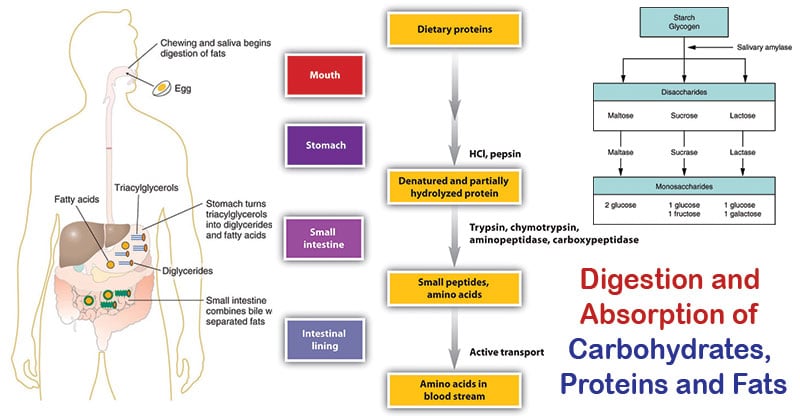



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Proteins And Fats




Learn About Carbohydrate Digestion Chegg Com




Chapter 24 Carbohydrates Carbohydrates Sugars And Their Derivatives



Carbs The Whole Truth Just A Pinch Recipes



Where Does The Digestion Of Carbohydrates Begin What Is The Process Quora




Atkins Most Carbohydrates Are Easily Broken Down By The Facebook



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Human Nutrition




Carbs In A Nutshell



Stage I Of Catabolism



Carbohydrates



1



What Do Complex Carbohydrates Break Down Into New Health Advisor




3 3 Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Medicine Libretexts




Carbohydrate Digestion Nutritional Doublethink




Monosaccharides An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Digestion Absorption And Transport In Digestive System



Www Naspghan Org Files Documents Pdfs Training Curriculum Resources Physiology Series Carbohydrate Digestion Naspghan Pdf




Carbohydrate Definition Classification Examples Britannica



Carbohydrates



Crossfit An Introduction To Metabolism



Carbohydrates
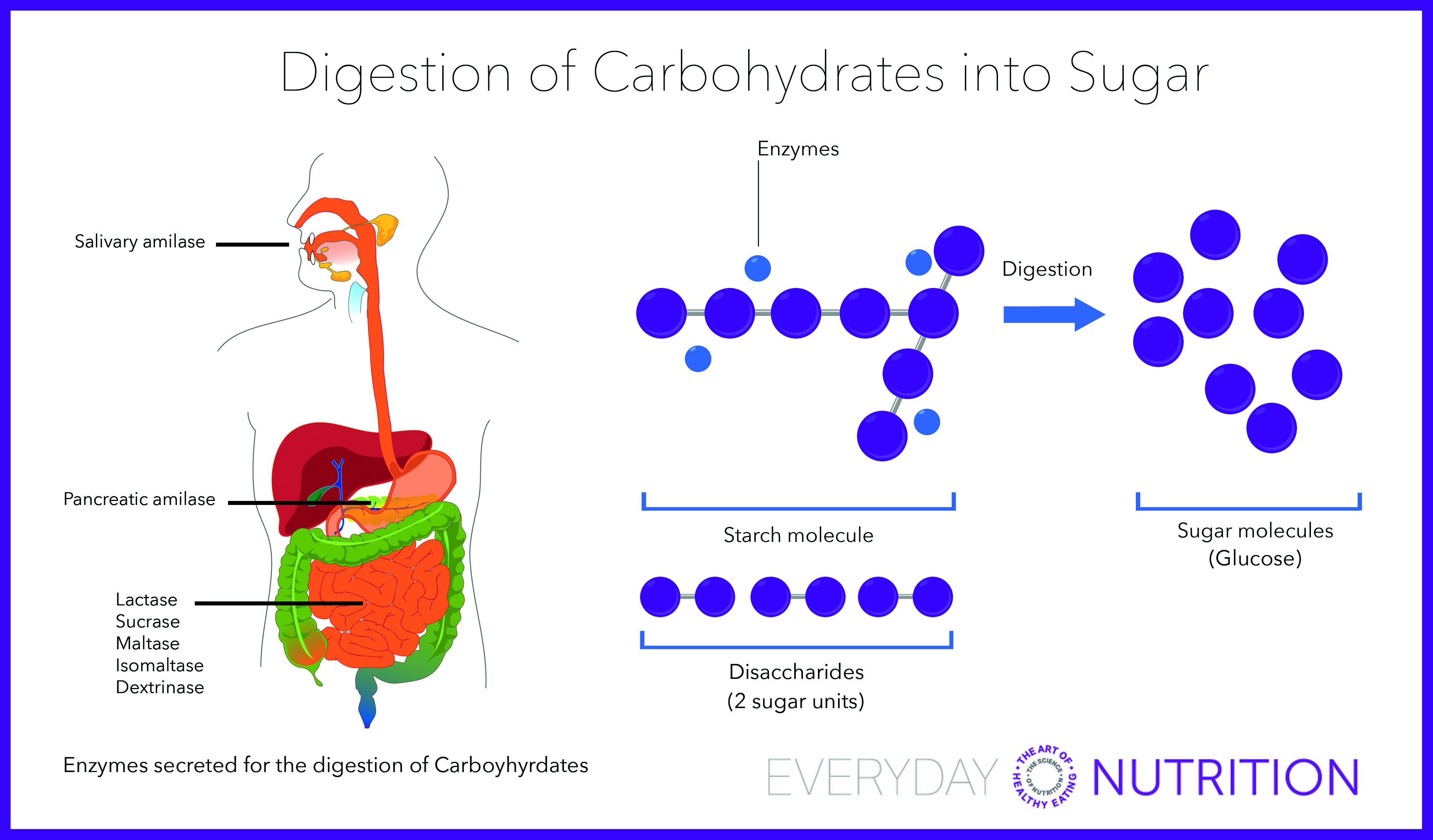



Everyday Nutrition Digestion Of Carbohydrates Into Sugar



Www Naspghan Org Files Documents Pdfs Training Curriculum Resources Physiology Series Carbohydrate Digestion Naspghan Pdf




Organic Compounds A Cracker Is Made Of Flour




Carbohydrates Metabolism Assays Biovision Inc




23 7 Chemical Digestion And Absorption A Closer Look Anatomy Physiology




The Truth About Carbs Insulin And Weight Loss Precision Nutrition



15 3 Digestive System Processes Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition




Chapter 4 Carbohydrates Sugar Starches And Fiber Carbohydrate




Carbohydrate Digestion Fermentation The Microbiome



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates




Carbohydrate Definition Classification Examples Britannica




Why Do You Need Food Food Provides Your Body With Materials To Grow And Repair Tissues It Provides Energy For Everything You Do Your Body Breaks Down Ppt Video Online Download




22 12b Chemical Digestion Of Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids And Nucleic Acids Medicine Libretexts




Computers 8 Worsley By Jose Villagra Carbohydrates The




Organic Compounds A Cracker Is Made Of Flour



Carbohydrates




What Are Carbohydrates A Concise Guide




Pin On Carbohydrates



Q Tbn And9gctdqnv1 Jayb1eej9ufgm1thzv2ycw71s1fhi2cn7p5wnvxwr K Usqp Cau



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿